What is DRM and How Does it Work?
Digital Rights Management (DRM) systems provide you with the ability to control how people can consume your content. Usually content owners and producers, like all the major Hollywood Studios and TV Stations, force content distributors to use specific DRM systems to protect each piece of content. Depending on the copyright requirements, Hollywood grade DRM protection is not always needed and sometimes it’s enough to provide basic protection through token based secure authentication or simple AES encryption of the video without sophisticated license exchange and policy management.
“Digital Rights Management (DRM) systems provide you the ability to control how people can consume your content”
How Does it Work?
A DRM setup needs specific encoding, packaging, playback and a license server. In the following sections we will describe each of these components in more detail.
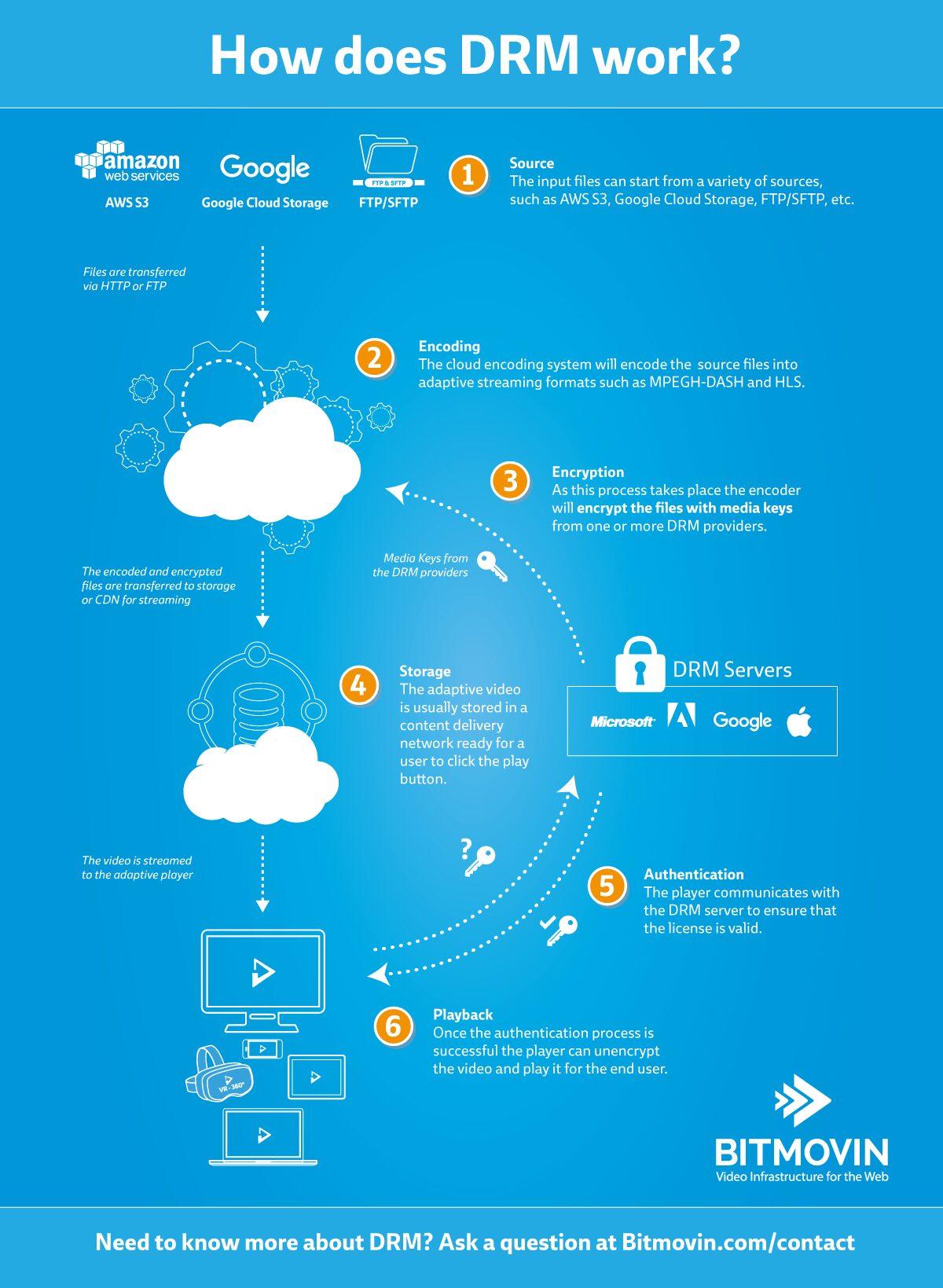
Bitmovin can provide the encoding, packaging and the player services as an out of the box solution.
License servers are offered by companies such as Irdeto, EZDRM, Expressplay and Axinom who provide a Multi-DRM License Server setup. It’s also possible to build your own license servers and negotiate terms directly with Google (Widevine), Microsoft (PlayReady), Adobe (PrimeTime) or Apple (Fairplay), but it usually takes longer.
Encoding & Packaging
From an encoding and packaging point of view, it does not make much difference whether the video is ‘just’ AES encrypted or Hollywood grade DRM encrypted because, for the encryption, AES is used in both cases. The major difference is that for Hollywood grade DRMs further metadata information needs to be added in the packaging step. Hollywood grade DRMs such as PlayReady, Widevine, PrimeTime and Fairplay don’t differ on the encryption side, they differ on the configuration features that are provided. Features such as offline playback, fine grained policies (e.g., allow only SD playback, rights visibility for users, APIs, different payment modes such as subscription, purchase, rental, gifting, etc.) and platforms that are supported (e.g., Chrome, Firefox, IE, Safari, Android, iOS, etc.).
Multi-DRM with MPEG-CENC
Typically, each device supports just one DRM. If you want to achieve maximum device reach it’s impossible to use just one DRM. You need to use multiple DRM’s in parallel. The MPEG Common Encryption (MPEG-CENC) standard enables this in the most efficient way as it allows key association from different DRM’s with the same video. This means that your video can be encoded and encrypted once with the same key. Metadata for the different DRM’s will be added in the packaging step. The details of the license acquisition, license mappings, etc. will be left up to the individual DRM system. The player decides, based on the platform support, which specific DRM will be used.
“If you want to achieve maximum device reach, it’s impossible to use just one DRM, you need to use multiple DRM’s in parallel”
Traditional Multi-DRM setups need to encrypt and package the content for each DRM differently. This increases the storage footprint of the content as each video needs to be encrypted and packaged with every DRM system and stored separately. Each video also needs to be encoded into multiple resolutions and bitrates to serve different devices and then each encoding needs to be encrypted and packaged with all the different DRMs. This would not only increase the storage footprint tremendously, it also increases the management efforts, because somebody needs to keep track of these multiple different versions. Beside that it reduces the efficiency of your CDN as so many different versions of the same content are distributed.
Playback
On the player side it’s possible to utilize the HTML5 Encrypted Media Extensions (EME) to enable DRM playback without plugins. If the DRM is not supported through the EME you could fallback to Flash and Adobe Access, if supported by your player vendor. On the other hand, if the content is MPEG-CENC Multi-DRM encrypted, the player could automatically choose the DRM that is natively supported on the given platform to playback the content in HTML5 without plugins. The authentication and the license acquisition will be handled by the player through the EME with the metadata that is provided with the content.
“On the player side it’s possible to utilize the HTML5 Encrypted Media Extensions (EME) to enable DRM playback without plugins”
Licensing Server
The licensing server is the management backend of your DRM setup. It allows you to create, modify and revoke licenses for your content and users. Licensing servers and DRM’s differ in their features such as offline playback, fine grained policies, rights visibility for users, APIs, different payment (subscription, purchase, rental and gifting), etc. License servers are provided by several companies such as Irdeto, EZDRM, Expressplay, Axinom, etc. It’s also possible to create your own licensing backend if you have a contract with Google (Widevine), Microsoft (PlayReady), Adobe (PrimeTime) or Apple (Fairplay) directly and you implement the specification. As long as your licensing server follows the specifications, it could be integrated with the other parts of the DRM chain, e.g., encoding, packaging and playback.
Hollywood & UltraViolet
When implementing a DRM strategy you should check that the DRM is accepted by the content owner. Which means that if you distribute Hollywood content you need to implement a DRM that is accepted by the Hollywood studios. But also if you don’t deliver Hollywood content, it’s good to check what is accepted by Hollywood, because you never know – you will probably deliver such content in the future. Replacing an already deployed DRM solution is hard and Hollywood has already done the due diligence of the DRMs for you, so it’s worth checking these recommended DRMs.
“When implementing a DRM strategy you should check that the DRM is accepted by the content owner”
The Digital Entertainment Content Ecosystem (DECE) is a consortium of 85 companies (e.g., studios, manufactures, etc.) which created the UltraViolet standard that ensures that after you purchase a content you are able to watch this content on broad number of devices. DRM is a major part of UltraViolet and therefore six DRM technologies have been approved:
- Widevine
- PlayReady
- PrimeTime
- Marlin
- OMA
- DivX DRM
Apple Fairplay is not part of this list as Apple is not a member of the DECE and Fairplay has just entered the market.
Basic Encryption
A Hollywood grade DRM is not always needed, sometimes it’s enough to just add another layer of security through AES encryption. Apple HTTP Live Streaming (HLS) and MPEG Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP (MPEG-DASH) both support this use case.
- HLS AES Encryption
- Apple HLS supports two encryption methods:
- AES-128
- SAMPLE-AES
AES-128 encrypts the whole segment with the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) using a 128 bit key, Cipher Block Chaining (CBC) and PKCS7 padding. The CBC will be restarted with each segment using the Initialization Vector (IV) provided.
“A Hollywood grade DRM is not always needed, sometimes it’s enough to just add another layer of security through AES encryption”
SAMPLE-AES encrypts each individual media sample (e.g., video, audio, etc.) by itself with AES. The specific encryption and packaging depends on the media format, e.g., H.264, AAC, etc. SAMPLE-AES allows fine grained encryption modes, e.g., just encrypt I frames, just encrypt 1 out of 10 samples, etc. This could decrease the complexity of the decryption process. There are several advantages to this approach as fewer CPU cycles are needed and, for example, mobile devices need less power consumption, higher resolutions can be effectively decrypted, etc.
DASH Clear Key Encryption
Clear Key encryption is an interface supported by EME. This interface can be used to deliver MPEG-DASH content with Clear Key. The interface provides the basic functionality that the user could provide a key that will be used for the decryption of the segments. MPEG-DASH signals the key in the Media Presentation Duration (MPD), which is the manifest of MPEG-DASH. All the relevant information that is needed for decryption is included in the MPD.
DRM Systems
If DRM is a requirement for your project you should take a look at the following major DRM systems. Microsoft, Google, Adobe and Apple provide high profile DRM systems with various features. In the end you will probably end up with a Multi-DRM setup where you utilize several or all of these DRMs in parallel to reach all the major devices.
“In the end you will probably end up with a Multi-DRM setup where you utilize several or all of these DRMs in parallel to reach all the major devices”
Video technology guides and articles
- Back to Basics: Guide to the HTML5 Video Tag
- What is a VoD Platform?A comprehensive guide to Video on Demand (VOD)
- Video Technology [2022]: Top 5 video technology trends
- HEVC vs VP9: Modern codecs comparison
- What is the AV1 Codec?
- Video Compression: Encoding Definition and Adaptive Bitrate
- What is adaptive bitrate streaming
- MP4 vs MKV: Battle of the Video Formats
- AVOD vs SVOD; the “fall” of SVOD and Rise of AVOD & TVOD (Video Tech Trends)
- MPEG-DASH (Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP)
- Container Formats: The 4 most common container formats and why they matter to you.
- Quality of Experience (QoE) in Video Technology [2022 Guide]




